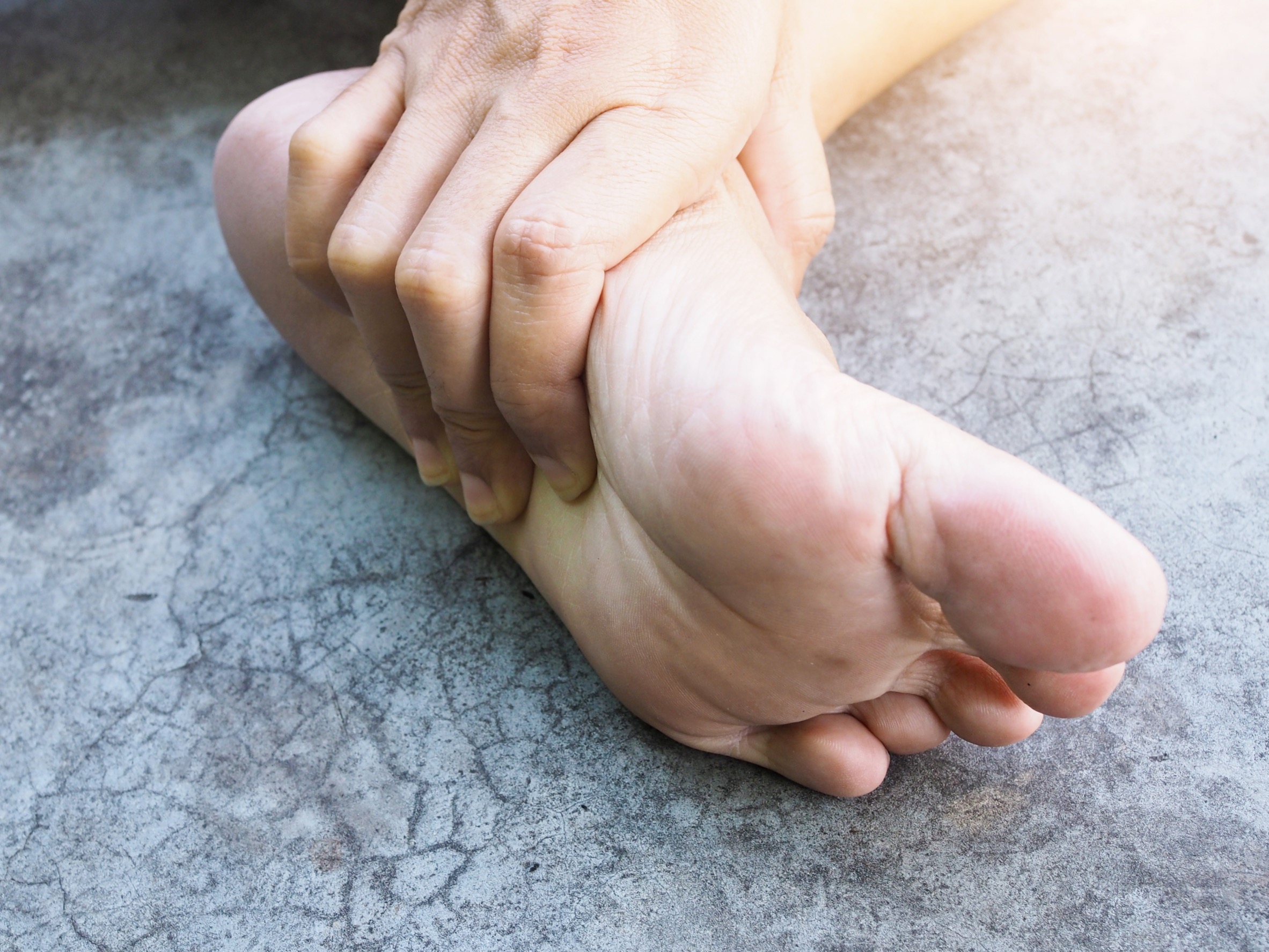
What is gout?
If you have experienced pain, redness, swelling, and heat of your toe joint, most often in the joint of the big toe, it is possible you have gout. Gout is a common type of arthritis that causes a great deal of pain. Gout is caused by an excess of something in your body called uric acid. When there is too much uric acid in the body, it begins to form crystals in the joints. These uric acid crystals can feel like tiny, sharp shards. Hence why gout is so painful! Once these crystals build up in the joint, it becomes red, swollen, hot, and filled with pain. Gout often occurs in only one joint at a time and usually in the big toe joint, but also can occur in other joints of the toes, ankles, or knee joints. People with gout may experience periods of time where they have no symptoms (called remission) and other times where their symptoms get worse. These periods of time where people with gout get symptoms and pain, often all of a sudden, are called gout flares or gout attacks.
Some factors out of our control, like genetics and gender, play a role in the amount of uric acid you have. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), men are more likely to experience gout than women. Other factors that contribute to gout can be controlled. These include diet, weight loss, staying hydrated, and limiting alcohol consumption. Foods that can contribute to gout and should be limited include red meats, organ meats, and certain seafoods. These foods contain high levels of purines, which contribute to increased uric acid when your body breaks these compounds down.
How do you treat gout?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for gout, but there are medications to help treat gout. Treatment for gout depends on whether you are experiencing a current flare, versus if you have managed to get past the flare and need preventive treatment.
Medications that can help relieve pain and inflammation during a gout attack include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as indomethacin (Indocin), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), and naproxen (Aleve). Colchicine is a prescription medication used at the first sign of a gout flare to help with inflammation and pain. Colchicine is also used to help prevent future gout flares in some cases as well. In some cases, prescription corticosteroids (ex. Prednisone) can be prescribed to help with the inflammation and pain of an acute gout attack. These medications are used while someone is experiencing a gout attack, usually at the first sign of the flare.
Other medications can be used to help reduce the occurrence of gout attacks. These medications include prescription medications such as allopurinol (Zyloprim), febuxostat (Uloric), and pegloticase (Krystexxa) most commonly. These medications are aimed at lowering the amount of uric acid in the body. They are usually taken long-term to prevent future gout flares.
Not all medications are right for everyone. If you have other health conditions like kidney or liver disease, or take certain medications, there may be gout medicines you should not take. Medication regimens to treat gout should be individualized and determined in consultation with your health care provider for your unique situation. If you’re experiencing symptoms of gout, you should speak with your health care provider.
Disclaimer: This blog is written for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read or seen online.
Resources
1) https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/types/gout.html
2) https://www.arthritis.org/diseases/gout