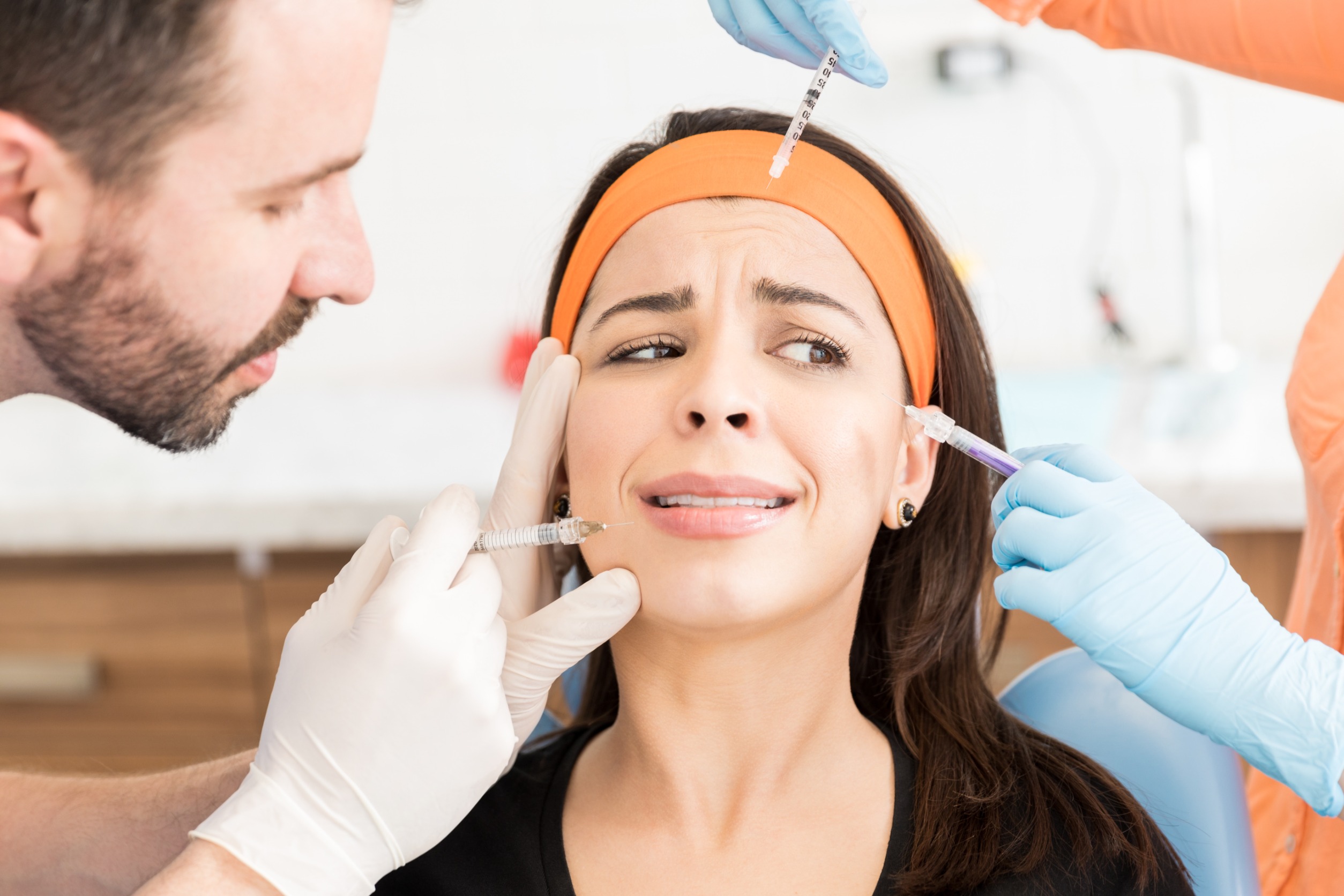
Botulinum toxin, most commonly known as Botox, is a well-known cosmetic treatment used to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. However, botulinum toxins are more than just a cosmetic treatment. In fact, they have been used for various medical indications, such as muscle spasms, chronic migraine, and hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). In this blog post, we’ll delve into Botox and its medical uses.
What are Botulinum Toxins?
Botulinum toxins are a type of neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. These toxins work by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that communicates messages between nerve cells and muscles. When acetylcholine release is blocked, the muscles become temporarily paralyzed, leading to a range of effects depending on the medical indication being treated. Botox is the most commonly known version of the botulinum toxins. However, there are other types of botulinum toxins such as Dysport, Xeomin, and Myobloc. This blog will specifically focus on Botox as the different versions of these toxins often have different FDA approved uses and niches. Botox’s technical drug name is onabotulinumtoxinA.
Medical Indications for Botox:
Muscle Spasms: Botulinum toxins can be used to treat muscle spasms, such as those associated with cervical dystonia (a condition causing neck muscle spasms) or spasticity (muscle stiffness and spasms due to neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis). The injections work by reducing muscle contractions and spasms.
Chronic Migraine: Botulinum toxins have been FDA-approved for the treatment of chronic migraine. Injections are typically administered every 12 weeks and work by blocking the release of pain-signaling chemicals called neurotransmitters. Read our blog on The Top Migraine Medications
Hyperhidrosis: Botulinum toxins can be used to treat excessive sweating, a condition called hyperhidrosis. The injections work by blocking the neurotransmitters responsible for activating sweat glands, leading to reduced sweating.
Blepharospasm: Botulinum toxins can be used to treat blepharospasm, a condition causing uncontrollable eye twitching or spasms. The injections work by relaxing the muscles around the eye, reducing twitching and spasms.
Overactive Bladder: Botulinum toxins can be used to treat overactive bladder, a condition causing frequent urination and urgency. The injections work by relaxing the muscles in the bladder, reducing the frequency and urgency of urination.
Considerations for Botulinum Toxin Use
While botulinum toxins are generally safe and well-tolerated, there are some considerations to keep in mind. First and foremost, botulinum toxins should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or allergies may not be suitable candidates for botulinum toxin treatment. It’s important to discuss any medical conditions or concerns with your healthcare provider before undergoing treatment.
In conclusion, Botox is more than just a cosmetic treatment. It has a range of medical uses and can be effective in treating various conditions such as muscle spasms, chronic migraine, hyperhidrosis, blepharospasm, and overactive bladder. If you’re considering botulinum toxin treatment for a medical indication, be sure to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your healthcare provider to determine if it’s the right choice for you.
Resources:
1) Nigam PK, Nigam A. Botulinum toxin. Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55(1):8-14. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.60343. PMID: 20418969; PMCID: PMC2856357.
2) Botox (onabotulinumtoxin A) [package insert]. Irvine, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2010.
3) Mayo Clinic. Botox Injections; Nov 2022. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/botox/about/pac-20384658
Vaccines for Cold & Flu Season
Fall is upon us, which means cold and flu season is also lurking in its shadows. While there has already been a wave...