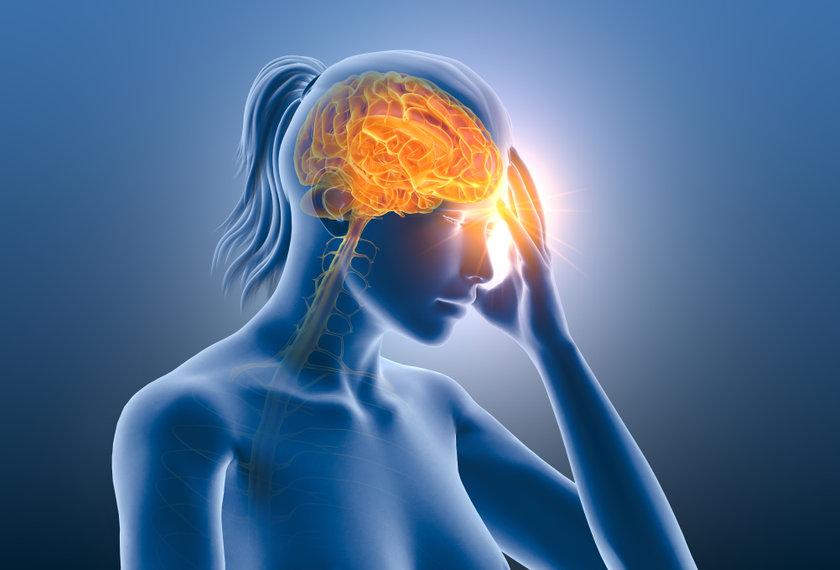
What is a migraine?
A migraine is a reoccurring, disabling type of headache that is both common and unique. The classic migraine headache usually occurs on just one side of the head and causes a throbbing or pulsating pain. Migraine headaches are frequently accompanied by nausea and vision disturbances. Episodes might range from fairly minor to very severe. The majority of migraine sufferers have recurrent headache attacks that can occur for years. If migraines occur less than fourteen times per month, it is called ‘episodic’. If someone experiences more than 15 migraine attacks per month, it is considered ‘chronic’.
Migraines affect 12-15% of the general population. Migraine headaches appear in roughly half of those people throughout childhood and may run in the family. They are more common in women than men, possibly due to the influence of hormones.
What can you do for migraines?
Migraines can be difficult to treat. It is said that migraine treatments only work 50% of the time, so finding the right treatment may just be a process of trial and error. Treatment also may depend on things like the frequency, severity, and duration of migraine attacks. There are two different ways migraines can be treated. You can either take medication daily to prevent migraines (preventative) or take medication only when you begin to experience a migraine (acute).
Also read our blog about Top Migraine Medications
For a long time, the mainstay of acute migraine treatment included only a class of medicines called ‘triptans’ (ex. Sumatriptan, rizatriptan, eletriptan, etc.). However, not everyone gets good relief from these medicines. Other times people may not tolerate the triptan medications or have contraindications to taking them. If used regularly, or more than twice weekly, there is also a possible “medication-overuse headache” (or rebound headache) associated with triptans. It is said there may be up to 30% of people who don’t respond or cannot use these medications. There are several newly FDA-approved agents for acute migraine treatment.
These include:
- Lasmiditan (Reyvow®) – Serotonin 1F receptor agonists (ditan)
- Rimegepant (Nurtec ODT®) – CGRP receptor blockers (gepants)
- Ubrogepant (Ubrelvy®) – CGRP receptor blockers (gepants)
Newer medicines like Nurtec ODT® and Ubrelvy® (gepants) do not have the risk of medication overuse headaches like the triptans do. Although, right now there are no studies directly comparing these new medications to our standard therapy (triptans), so it’s hard to say if one option is better than the other. The best migraine treatment for each person is based on personal response and will likely be a process of trial and error. Finding a treatment that works for you can be a tough process for migraine sufferers. However, with new agents to try, finding the best treatment for you may be closer than you think! Talk with your healthcare provider to find out if one of these agents is right for you.
Save up to 80% on the cost of your prescriptions at your local pharmacy with EasyDrugCard.com. Download your free drug card and begin saving today.
Resources:
- Pharmacytoday.org